Άλγεβρα Lie


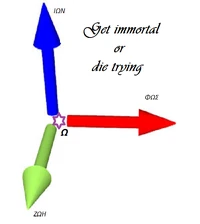
Lie group is an analytic manifold with a group structure such that the group operations are analytic. Lie groups arise in a natural way as transformation groups of geometric objects. The tangent space g at the identity element of a Lie group G has a rule of composition (X,Y)→[X,Y] derived from the bracket operation on the left invariant vector fields on G. The vector space g with this rule of composition is called the Lie algebra of G. The structures of g and G are related by the exponential mapping exp: g → G which sends straight lines through the origin in g onto one-parameter subgroups of G (see Fig 1). The power of using Lie algebra, due to its linearity, the object moves along a geodesic without deforming its shape.

Ομάδα Lie
Representation of the relation between the Lie group and the Lie algebra. The Lie algebra (red plane) is the tangent space to the Lie group's manifold (here represented as a blue sphere) at the identity. Through the exponential map, each straight path through the origin on the Lie algebra produces a path over the manifold which runs along the respective geodesic. Conversely, each element of the group has an equivalent in the Lie algebra. This relation is so profound that (nearly) all operations in the group, which is curved and nonlinear, have an exact equivalent in the Lie algebra, which is a linear vector space. Though the sphere in R^3 is not a Lie group (we just use it as a representation that can be drawn on paper), that in R^4 is, and describes the group of unit quaternions.
σκελετός

Αλγεβρική Ομάδα
Γενική Γραμμική Ομάδα
Ορθογώνια Ομάδα
Μοναδιακή Ομάδα
Μαθηματική Αναπαράσταση
Μαθηματική Μήτρα
- Ένα Μαθηματικό Δόμημα.
Ετυμολογία[]
Η ονομασία "Άλγεβρα Lie" σχετίζεται ετυμολογικά με το όνομα "Lie".
Εισαγωγή[]
In mathematics, a Lie algebra (pronounced "Lee") is a vector space over a field F together with a non-associative, alternating bilinear map , called the Lie bracket, satisfying the Jacobi identity.
Lie algebras are closely related to Lie groups, which are groups that are also smooth manifolds, with the property that the group operations of multiplication and inversion are smooth maps. Any Lie group gives rise to a Lie algebra.
Conversely, to any finite-dimensional Lie algebra over real or complex numbers, there is a corresponding connected Lie group unique up to covering (Lie's third theorem). This correspondence between Lie groups and Lie algebras allows one to study Lie groups in terms of Lie algebras.
Lie algebras were so termed by Hermann Weyl after Sophus Lie in the 1930s. In older texts, the name infinitesimal group is used.
History[]
Lie algebras were introduced to study the concept of infinitesimal transformations by Lie in the 1870s, and independently discovered by Wilhelm Killing in the 1880s.
Definitions[]
A Lie algebra is a vector space over some field F allows more generally for a module over a commutative ring together with a binary operation called the Lie bracket that satisfies the following axioms:
- for all scalars a, b in F and all elements x, y, z in .
- for all x in .
- The Jacobi identity,
- for all x, y, z in .
Using bilinearity to expand the Lie bracket and using alternativity shows that for all elements x, y in , showing that bilinearity and alternativity together imply
- for all elements x, y in . If the field's characteristic is not 2 then anticommutativity implies alternativity.
It is customary to express a Lie algebra in lower-case fraktur, like . If a Lie algebra is associated with a Lie group, then the spelling of the Lie algebra is the same as that Lie group. For example, the Lie algebra of SU(n) is written as .
Generators and dimension[]
Elements of a Lie algebra are said to be generators of the Lie algebra if the smallest subalgebra of containing them is itself.
The dimension of a Lie algebra is its dimension as a vector space over F.
The cardinality of a minimal generating set of a Lie algebra is always less than or equal to its dimension.
Υποσημειώσεις[]
Εσωτερική Αρθρογραφία[]
- Ομάδα
- Ομαδοθεωρία
- Ορθογώνια Ομάδα
- Μοναδιακή Ομάδα
- Ετεροτική Ομάδα
- Αναπαράσταση
- Μήτρα
- Μεταθετική Άλγεβρα
Βιβλιογραφία[]
Ιστογραφία[]
Ομώνυμο άρθρο στην Βικιπαίδεια
- Ομώνυμο άρθρο στην Livepedia
- math.upenn.edu
- Geometric Particle Filter
- Representation of the relation between the Lie group and the Lie algebra
- How is a Lie Algebra able to describe a Group
|
Αν και θα βρείτε εξακριβωμένες πληροφορίες "Οι πληροφορίες αυτές μπορεί πρόσφατα Πρέπει να λάβετε υπ' όψη ότι Επίσης, |
- Μην κάνετε χρήση του περιεχομένου της παρούσας εγκυκλοπαίδειας
αν διαφωνείτε με όσα αναγράφονται σε αυτήν
- Όχι, στις διαφημίσεις που περιέχουν απαράδεκτο περιεχόμενο (άσεμνες εικόνες, ροζ αγγελίες κλπ.)

![{\displaystyle {\mathfrak {g}}\times {\mathfrak {g}}\rightarrow {\mathfrak {g}};(x,y)\mapsto [x,y]}](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/50c38849c1e1b764ed5701a1d5a2ad58b04c5a12)
![{\displaystyle [\cdot ,\cdot ]:{\mathfrak {g}}\times {\mathfrak {g}}\to {\mathfrak {g}}}](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/b2f1416dc3f237962df1d1276fa15aa971117e2d)
![{\displaystyle [ax+by,z]=a[x,z]+b[y,z],\quad [z,ax+by]=a[z,x]+b[z,y]}](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/f9444ab21739412fb95379e4845f606e9e33f5b5)
![{\displaystyle [x,x]=0\ }](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/17bd6c93ea35288bdd86daaa0cd5425947ed8a81)
![{\displaystyle [x,[y,z]]+[z,[x,y]]+[y,[z,x]]=0\ }](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/aea92bdbb80c51c58ebdcd00e2006749219fad2f)
![{\displaystyle [x+y,x+y]}](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/eee068639ac11f24cf91a306968ab264a1651b79)
![{\displaystyle [x,y]+[y,x]=0\ }](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/db71a2024ba1d63e4c0de5a718c2be1daad73720)
![{\displaystyle [x,y]=-[y,x],\ }](https://services.fandom.com/mathoid-facade/v1/media/math/render/svg/6cbae4efa682e26f900f8bd06f9e21ade41aecc9)